How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate flight maneuvers. Mastering drone operation requires understanding its components, adhering to safety regulations, and developing skillful control. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies responsibly and creatively, transforming you from a novice to a capable drone pilot.
We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone mechanics, from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques. Learn about the various drone components, their functions, and potential issues. We’ll cover safe takeoff and landing procedures, explain the relationship between joystick controls and drone movement, and discuss the importance of camera settings for optimal image capture. Finally, we’ll explore drone safety regulations, maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring you operate your drone safely and legally.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section details the function, importance, and potential issues associated with key drone components.
Major Drone Components and Their Functions
| Component | Function | Importance | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust, enabling flight and maneuverability. | Essential for lift and controlled movement. Different propeller designs affect flight characteristics. | Damage, imbalance, improper installation leading to vibrations or loss of control. |
| Motors | Spin the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. | Provide the power for flight; their performance directly impacts flight time and stability. | Motor failure, overheating, or burnout leading to crashes. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, controlling all aspects of flight, receiving input from sensors and sending commands to motors. | Crucial for stability, responsiveness, and autonomous flight functions. | Malfunction, software glitches, or sensor errors leading to erratic flight or loss of control. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Determines flight time; insufficient power can lead to premature landing or loss of control. | Depleted battery, damage, overheating, or short circuit causing sudden power loss. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for positioning and autonomous flight modes. | Essential for features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and precise waypoint navigation. | Weak signal, interference, or malfunction leading to inaccurate positioning or RTH failures. |
| IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) | Measures acceleration and rotation, providing data for stability and orientation. | Essential for smooth and stable flight, especially in GPS-denied environments. | Sensor drift, calibration issues, or damage leading to unstable flight. |
| Radio Transmitter/Receiver | Allows for remote control of the drone. | Enables pilot control over all aspects of the drone’s flight. | Signal interference, range limitations, or malfunction leading to loss of control. |
Drone Propeller Types and Their Impact
Drone propellers come in various sizes, pitches, and designs, each impacting flight performance differently. Larger propellers generally provide more thrust and lift, but may also reduce flight time. A higher pitch propeller increases speed but may reduce maneuverability. Propeller design also influences efficiency and noise levels. Understanding these differences is important for selecting the right propellers for a specific application.
Assembling a Basic Drone Kit
- Carefully unpack all components and verify their presence against the provided checklist.
- Attach the motors to the drone frame, ensuring proper alignment and secure fastening.
- Connect the propellers to the motors, paying close attention to the direction of rotation indicated on the propellers and motors.
- Mount the flight controller securely to the drone frame, connecting all necessary wires and sensors.
- Install and connect the battery to the flight controller.
- Connect the radio receiver to the flight controller.
- Power on the drone and perform initial calibration procedures as Artikeld in the drone’s manual.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents and equipment damage. This section details crucial pre-flight procedures and best practices.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Check battery level: Ensure the battery is fully charged and has sufficient power for the planned flight duration.
- Inspect propellers: Check for damage, cracks, or imbalances. Replace any damaged propellers.
- Verify GPS signal strength: Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. A weak signal can affect flight stability and accuracy.
- Inspect the drone frame: Check for any visible damage or loose parts.
- Test all control inputs: Verify that all control sticks and buttons are functioning correctly.
- Check surrounding environment: Ensure there are no obstacles or hazards in the flight area.
- Review local regulations: Confirm compliance with all applicable drone regulations and airspace restrictions.
Compass and IMU Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and IMU is crucial for accurate flight and stability. The compass provides directional information, while the IMU measures acceleration and rotation. Improper calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior, especially during takeoff and landing. Most drones provide an in-app calibration process that should be followed before each flight.
Choosing a Safe and Legal Flight Location
Selecting an appropriate flight location is paramount for safe drone operation. Factors to consider include airspace restrictions, proximity to obstacles and people, weather conditions, and legal regulations. Always check local airspace regulations and obtain necessary permits before flying. Avoid flying near airports, crowded areas, or sensitive infrastructure.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are critical for successful drone operation. This section Artikels proper techniques and common errors to avoid.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The specific procedures for takeoff and landing vary depending on the drone model and its flight modes. However, some general guidelines apply:
- Ensure a clear and safe takeoff and landing area, free from obstacles.
- Begin with a gentle throttle increase, allowing the drone to ascend smoothly and steadily.
- Maintain a stable and controlled ascent, avoiding sudden movements.
- For landing, initiate a slow descent using the throttle control, maintaining a steady approach.
- As the drone nears the ground, reduce the throttle gradually until it comes to a gentle stop.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques Comparison
Different drone models may employ varying takeoff and landing techniques. Some drones offer autonomous takeoff and landing features, simplifying the process. Others require more manual control and precise throttle management. Always refer to the drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Common Takeoff and Landing Errors
- Sudden throttle movements: This can lead to instability and loss of control.
- Inadequate pre-flight checks: Overlooking battery level, GPS signal, or propeller integrity can cause problems.
- Poor landing site selection: Landing in uneven terrain or near obstacles increases the risk of damage.
- Ignoring wind conditions: Strong winds can make takeoff and landing difficult and dangerous.
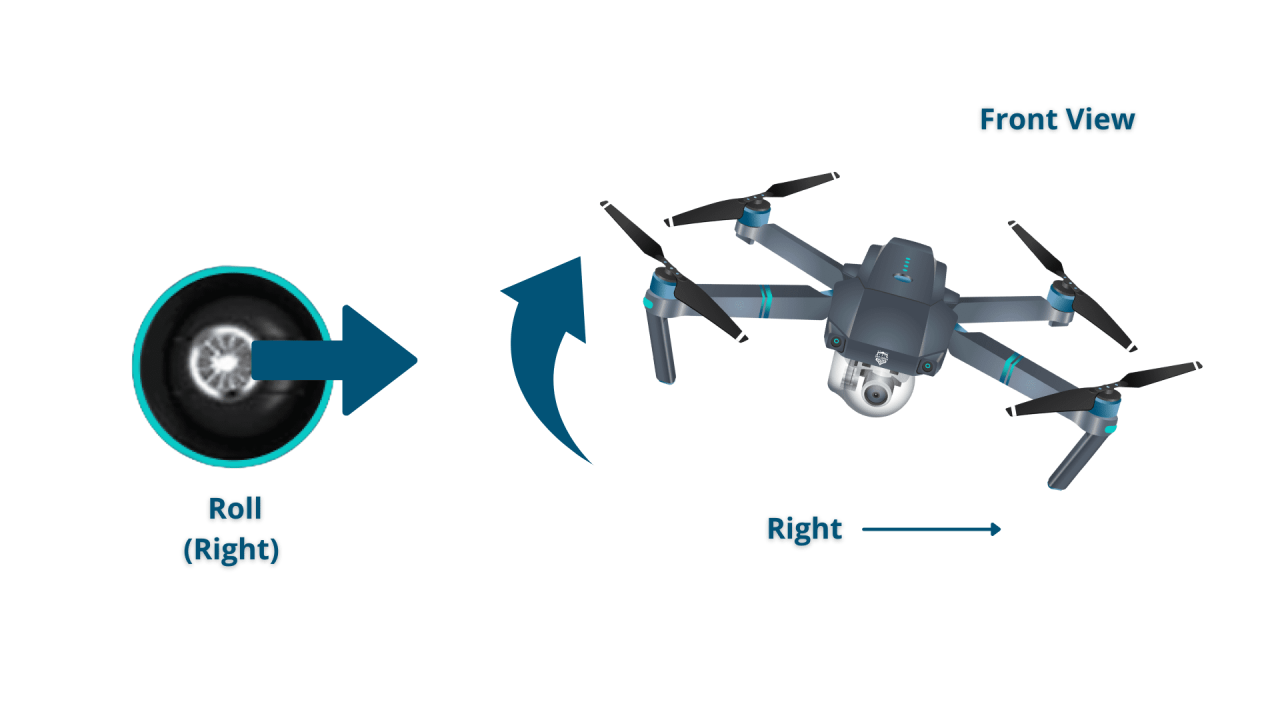
Controlling Drone Movement: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the relationship between joystick inputs and drone movement is essential for skillful drone operation. This section explains the control inputs and various flight modes.
Joystick Inputs and Drone Movement
| Joystick Direction | Drone Movement |
|---|---|
| Forward | Forward movement |
| Backward | Backward movement |
| Left | Leftward movement |
| Right | Rightward movement |
| Left Stick Up | Ascend |
| Left Stick Down | Descend |
| Right Stick Left/Right | Yaw (rotation around vertical axis) |
| Right Stick Forward/Backward | Pitch (forward/backward tilt) and Roll (side-to-side tilt) |
Flight Modes
Most drones offer various flight modes to cater to different skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode often restricts speed and maneuverability, while attitude mode provides more control. GPS mode enables features like Return-to-Home and waypoint navigation.
Drone Control in Windy Conditions
Windy conditions present significant challenges to drone control. Strong winds can push the drone off course, making it difficult to maintain stability. Mitigation strategies include reducing flight speed, flying in less windy areas, or using wind-resistant drone designs.
Drone Camera Operation
The camera is a key feature of many drones, enabling stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera features and settings is crucial for capturing high-quality images.
Drone Camera Features
Drone cameras vary in resolution, field of view (FOV), and image stabilization capabilities. Higher resolution provides greater detail, while a wider FOV captures more of the scene. Effective image stabilization minimizes blurring and improves image quality, especially during flight.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimizing camera settings for different lighting conditions is crucial for achieving high-quality images. ISO controls sensitivity to light, shutter speed determines exposure time, and aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens. Adjusting these settings based on the lighting conditions helps to avoid overexposed or underexposed images.
Comparison of Popular Drone Cameras
| Drone Model | Resolution | Field of View | Image Stabilization | Video Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Drone 1 | 48MP | 80° | 3-axis Gimbal | 4K at 60fps |
| Example Drone 2 | 20MP | 90° | Electronic Image Stabilization | 1080p at 30fps |
Drone Safety and Regulations

Adhering to drone safety guidelines and regulations is crucial for responsible and legal drone operation. This section highlights important safety practices and legal considerations.
Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location, encompassing airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. It is crucial to research and comply with all applicable regulations in your area before operating a drone. Failing to do so can result in penalties and legal repercussions.
Best Practices for Safe Drone Operation
- Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people.
- Never fly a drone near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Always be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards.
- Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions such as strong winds or rain.
- Keep the drone within visual line of sight.
- Do not fly over crowds or private property without permission.
Drone Accident Scenario and Prevention
Scenario: A drone crashes into a power line due to a loss of GPS signal in a high-wind situation. Prevention: Proper pre-flight checks, including GPS signal strength verification, and avoiding flight in high-wind conditions would have prevented the accident. Regular maintenance and firmware updates also contribute to minimizing malfunctions.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone. This section Artikels routine maintenance procedures and troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Routine Drone Maintenance
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight to remove dirt and debris.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use.
- Inspect the propellers for damage and replace them as needed.
- Check all connections and screws to ensure they are secure.
- Regularly update the drone’s firmware to benefit from bug fixes and performance improvements.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common malfunctions include motor failures, battery issues, GPS signal loss, and flight controller errors. Troubleshooting steps generally involve checking connections, replacing faulty components, calibrating sensors, and updating firmware. Refer to the drone’s manual for detailed troubleshooting guides.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations.
Importance of Firmware Updates
Regularly updating drone firmware is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Updates often include bug fixes, performance enhancements, and new features. Keeping the firmware up-to-date helps prevent malfunctions and ensures that the drone is operating at its best.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers

Once you’ve mastered basic drone control, you can explore advanced maneuvers. This section details how to perform these maneuvers safely and effectively.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal requirements, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and gain confidence in your piloting skills. This will help you to operate a drone safely and responsibly.
Performing Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips, rolls, and precise hovering, require practice and skill. Start by practicing in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people. Gradually increase the complexity of maneuvers as your skills improve. Always prioritize safety and avoid attempting maneuvers beyond your capabilities.
Drone Capabilities in Advanced Maneuvers
Different drones have varying capabilities in executing advanced maneuvers. Some drones are designed for acrobatic flight and offer a wider range of maneuvers, while others prioritize stability and ease of use. Choosing a drone that suits your skill level and intended use is important.
Safety Precautions for Advanced Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
- Practice in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people.
- Start with simpler maneuvers and gradually increase complexity.
- Always maintain control of the drone and be prepared to abort the maneuver if necessary.
- Ensure sufficient battery power before attempting advanced maneuvers.
- Check local regulations for any restrictions on acrobatic flight.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding composition, lighting, and various camera techniques. This section provides guidance on achieving professional-looking aerial content.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
- Plan your shots: Determine the desired composition, angles, and lighting conditions before taking off.
- Adjust camera settings: Optimize ISO, shutter speed, and aperture based on lighting conditions.
- Utilize drone features: Take advantage of features like gimbal stabilization and intelligent flight modes.
- Practice smooth movements: Avoid jerky movements that can blur images or videos.
- Edit your footage: Enhance your photos and videos using editing software to improve color, contrast, and sharpness.
Importance of Composition and Lighting
Composition and lighting are crucial for creating visually appealing aerial photos and videos. Effective composition involves arranging elements within the frame to create a visually balanced and interesting image. Proper lighting enhances the mood and atmosphere of the shot.
Examples of Aerial Shots
Cinematic shots involve smooth, sweeping movements to create a dynamic and engaging visual experience. Aerial panoramas stitch together multiple images to create a wide-angle view of a scene. Other shots include establishing shots, close-ups, and tracking shots, each providing a unique perspective.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience that blends technology, skill, and creativity. By understanding the fundamentals of drone mechanics, adhering to safety protocols, and mastering flight control, you can unlock a new perspective on the world. Remember, responsible operation is paramount. Embrace the learning process, practice diligently, and always prioritize safety. With this guide as your companion, you are well-equipped to embark on your aerial adventures, capturing stunning visuals and exploring the boundless possibilities of drone technology.
FAQ
What is the maximum flight time of a typical drone battery?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model and battery size, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to return the drone to its home point if possible. If unsuccessful, contact local authorities to report the lost drone and its location.
What are the common causes of drone crashes?
Common causes include low battery, pilot error, mechanical failure, and adverse weather conditions.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced interference.
